The bearded dragon, scientifically known as Pogona, is a popular reptile species kept as pets by many enthusiasts. These captivating creatures possess a unique feature called the “third eye.” In this article, we will explore the intriguing world of the Bearded Dragon Third Eye, understanding its purpose, functions, and significance in their lives. Let’s dive in and uncover the mysteries behind this remarkable adaptation.
What is the Third Eye of a Bearded Dragon?
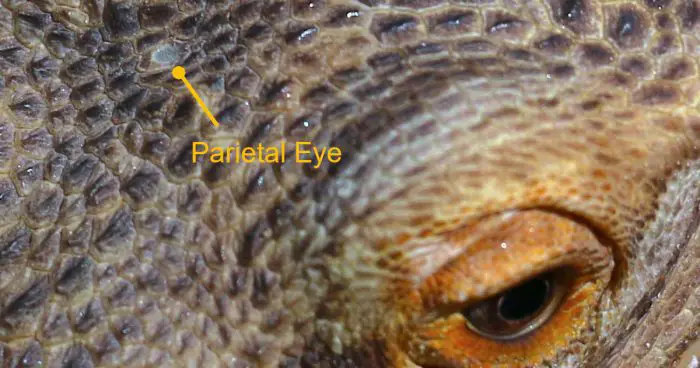
The Bearded Dragon Third Eye of refers to a unique parietal eye, also known as the pineal eye, located on the top of the head. This specialized organ is not a functional eye in the traditional sense but rather a light-sensitive structure that plays various important roles in their lives.
Evolutionary Background
The presence of the third eye in bearded dragons can be traced back to their evolutionary history. Similar to other reptiles, they are descendants of ancient reptilian ancestors who possessed a well-developed parietal eye. Over time, as evolution shaped their physiology, the third eye became less functional in terms of visual perception but retained its light-sensing capabilities.
Physical Characteristics of the Third Eye
The bearded dragon’s third eye is characterized by a round shape with a translucent scale covering its surface. Unlike their primary eyes, it lacks an eyelid and cannot focus or perceive detailed images. However, it is highly sensitive to changes in light intensity.
Location and Structure
Situated at the top of the bearded dragon’s head, the third eye is positioned between the two primary eyes. It is easily recognizable due to its distinct scale and pigmentation, often appearing as a lighter or darker spot compared to the surrounding skin. The eye is connected to the brain through a specialized neural pathway.
Role in Thermoregulation
One of the primary functions of the bearded dragon’s third eye is thermoregulation. It helps them regulate their body temperature by sensing variations in light intensity. When exposed to direct sunlight or artificial UV light sources, the third eye detects the changes and assists in adjusting their basking behavior, ensuring optimal heat absorption.
Light Perception and Circadian Rhythm
The third eye also plays a crucial role in perceiving light, which aids in establishing the bearded dragon’s circadian rhythm. Light exposure received through the third eye helps them differentiate between day and night, influencing their activity levels and biological processes.
Implications for Sleep Patterns
Studies suggest that the third eye’s sensitivity to light affects the bearded dragon’s sleep patterns. As crepuscular creatures, they are more active during dawn and dusk. The third eye assists in signaling the transitioning periods of the day, allowing the bearded dragon to adjust their sleep-wake cycles accordingly
Protection and Predator Awareness
The third eye serves as an essential tool for predator awareness and protection. Its light-sensing capabilities enable the bearded dragon to detect potential threats from above, such as birds of prey or other predators. This heightened awareness allows them to respond quickly and take evasive actions to ensure their safety.
Influence on Social Behavior
The third eye also plays a role in the social behavior of bearded dragons. It is believed that the eye’s sensitivity to light influences the perception of other individuals and their surrounding environment. This may contribute to their communication, territorial displays, and mating rituals.
Sensitivity to Environmental Changes
Bearded dragons are known for their adaptability to various environments. The third eye enhances its ability to sense environmental changes, such as shifts in light intensity or temperature. This heightened sensitivity allows them to respond and adapt swiftly to ensure their survival in diverse habitats.
The Role of the Pineal Gland
The pineal gland, located near the third eye, is responsible for regulating various physiological processes, including hormone production and the sleep-wake cycle. It is closely connected to the third eye’s light-sensing abilities, and together they contribute to the overall well-being and functioning of the bearded dragon.
Health Indicators and Eye Health
The appearance and condition of the Bearded Dragon Third Eye can provide valuable insights into the overall health of a bearded dragon. A healthy third eye is clear, vibrant, and free from abnormalities. Any changes, such as cloudiness, swelling, or discoloration, may indicate underlying health issues that require attention from a reptile veterinarian.
Potential Disorders and Health Concerns
While the third eye is a remarkable adaptation, it is not immune to certain disorders or health concerns. Some bearded dragons may experience issues such as third eye dystrophy, where the eye becomes non-functional or develops abnormalities. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper husbandry practices can help prevent and address these concerns.
Caring for Bearded Dragon Third Eye
To ensure the well-being of the third eye and the overall health of a bearded dragon, proper care is essential. Providing a suitable habitat with appropriate lighting, temperature gradients, and a balanced diet is crucial. Regular monitoring of the third eye’s appearance and seeking professional advice when necessary are important steps in maintaining optimal health.
Conclusion
The Bearded Dragon Third Eye is a fascinating adaptation that adds to the allure of these captivating reptiles. Although it no longer functions as a visual organ, its light-sensing capabilities serve multiple important purposes. From thermoregulation and circadian rhythm to predator awareness and social behavior, the third eye contributes significantly to their survival and well-being.
As responsible pet owners, understanding the significance of the bearded dragon’s third eye allows us to provide the best possible care for these incredible creatures. By ensuring their environment is conducive to their instincts and health requirements, we can create a thriving and enriching life for our bearded dragon companions.
FAQs (Bearded Dragon Third Eye)
No, the third eye does not have the same visual capabilities as the primary eye. It primarily senses changes in light intensity and assists in regulating various physiological functions.
While the third eye does not need specific care, regular monitoring of its appearance and seeking veterinary attention for any abnormalities is important to ensure the bearded dragon’s well-being.
The third eye of a bearded dragon is relatively resilient, but it can be affected by certain conditions or injuries. It is essential to provide a safe and suitable environment to minimize the risk of any harm coming to the third eye.
Yes, all bearded dragons have a third eye. However, the visibility of the eye can vary among individuals. Some may have a more pronounced and visible third eye, while others may have a less noticeable one.
Any changes in the appearance of the third eye should be carefully observed. If you notice significant abnormalities, such as swelling, discharge, or persistent cloudiness, it is advisable to consult a reptile veterinarian for proper evaluation and guidance.
